Refer to Figure 13-1. Ceteris paribus, an increase in personal income taxes would be represented by a movement from
A) AD1 to AD2. B) AD2 to AD1. C) point A to point B. D) point B to point A.
B
You might also like to view...
John is trying to decide how to divide his time between his job as a stocker in the local grocery store, which pays $7 per hour for as many hours as he chooses to work, and cleaning windows for the businesses downtown. He makes $2 for every window he cleans. John is indifferent between the two tasks, and the number of windows he can clean depends on how many hours he spends cleaning in a day, as shown in the table below:Hours PerDay CleaningWindowsTotal Numberof WindowsCleaned0017211314416517A second hour cleaning windows will yield additional earnings of ________.
A. $8 B. $7 C. $14 D. $2
The price of a financial asset should equal the
A) present value of the payments to be received from owning the asset. B) future value of the payments to be received from owning the asset. C) face value of the asset less the future payments to be received from owning the asset. D) coupon value of the asset divided by the effective interest rate at the time the asset was purchased.
After a price change, the substitution effect will be the same as the income effect.
A. True B. False C. Uncertain
Figure 10-18
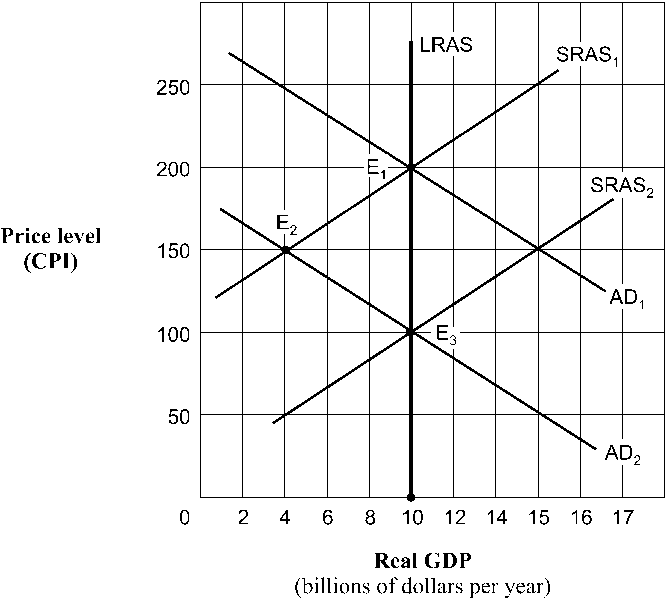
As shown in , the economy's point of short-run equilibrium, given by the shift of the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2, is
a.
E1.
b.
E2.
c.
E3.
d.
unable to be determined.