Why don't classical economists or monetarists advocate increasing the money supply in order to raise real GDP?
These economists believe that the economy already operates at full-employment GDP. Therefore, even
though they think than an increase in the money supply will lead to lower interest rates that will spur
investment and increase aggregate demand, they believe that the main result of this type of monetary
intervention will be inflation, since an increase in real production cannot occur.
You might also like to view...
Personnel economics is
A) the study of how workers are affected by tax law changes. B) the application of economic analysis to the hiring decision. C) the application of economic analyses to human resource issues. D) the study of the factors that determine wage rates.
The wage gap between high school and college graduates can be explained, other things the same, by ________
A) a greater increase in the demand for high school educated labor than college-educated labor B) a greater increase in the supply of college-educated labor than high school educated labor C) a greater increase in the demand for high school educated labor than in the supply of high school educated labor D) a greater increase in the demand for college-educated labor than high school educated labor
Brazil gives cash payments to its poor citizens on the condition that those citizens' children stay in school. In terms of the determinants of productivity, how might this public policy contribute to higher productivity in Brazil?
The maximum units of input you would possibly hire would be
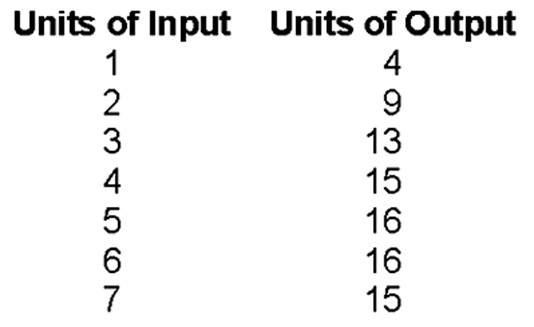
A. 3.
B. 4.
C. 5.
D. 6.