The price elasticity of the supply of teenage labor services is approximately 1.36. Suppose the minimum wage rises from $7.25 per hour to $8.75. Using the midpoint formula, what is the approximate change in the quantity of teenage labor supplied?
A) 7.3 percent
B) 14.4 percent
C) 25.5 percent
D) There is insufficient information to answer the question.
C
You might also like to view...
Each member in a group might do what's best for himself or herself instead of behaving in a way that optimizes the well-being of the entire group. This gives rise to the problem of:
A) Pareto inefficiency. B) free riding. C) irrational behavior. D) disequilibrium.
Why is it necessary for all economic systems to not only provide people with goods and services, but also restrict them from getting as much of these goods and services as they wish?
A) Failure to do this could lead to drastic shortages of goods and services. B) Failure to do this could reduce the efficiency of the system by producing some goods and services that are not as highly valued as others. C) Failure to do this could reduce efficiency and lead to an inequitable allocation of output. D) Failure to do this could lead to an inequitable allocation of goods and services produced.
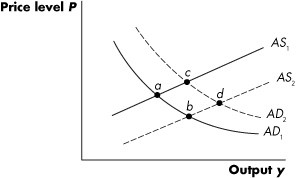
 Refer to Figure 14.2. A movement from point a to point b could be caused by a(n):
Refer to Figure 14.2. A movement from point a to point b could be caused by a(n):
A. increase in government spending. B. decrease in the price of oil. C. decrease in taxes. D. decrease in short-run aggregate supply.
Monopolistically competitive markets are different from perfectly competitive markets because in monopolistically competitive markets firms:
A. have some control over price, while in perfectly competitive markets firms have no control over price. B. face substantial barriers to entry, while in perfectly competitive markets firms face no significant barriers to entry. C. have no control over price, while in perfectly competitive markets firms have some control over price. D. sell a standardized product, while in perfectly competitive markets firms sell a differentiated product.