The rational expectations hypothesis suggests that
A) unanticipated fiscal policy actions are more powerful than monetary policy actions.
B) fiscal policy actions only work when accompanied by changes in the money supply.
C) anticipated monetary policy actions are more powerful than fiscal policy actions.
D) anticipated fiscal and monetary policy actions are not likely to achieve their stated aims.
D
You might also like to view...
Which of the following could generate economic profits for perfectly competitive firms in the short run, if they initially earn zero economic profits?
A) a fall in demand B) a unit tax on output C) an increase in total fixed costs D) a decrease in input prices
Which of the following would not be included in the measurement of GDP?
A) a bill from a car mechanic B) wages of a card dealer working in a Las Vegas casino C) commissions of a stockbroker D) the increased value of shares of stock E) c and d
Lewis has $5,000 worth of bonds in Farrell’s Seed Company. Bonnie has 10,000 shares of preferred stock in the company, Jeff has 100,000 shares of common stock, and Val has 1 share of common stock. If Farrell’s Seed Company goes out of business, which obligation will it be required to meet first?
a. paying Bonnie the full value of her preferred stock b. paying Jeff the dividends on his common stock c. paying Lewis the full value of his bonds d. paying Val the full value for her share of common stock
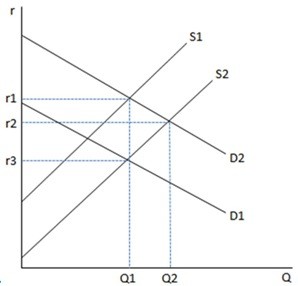 Considering the market for loanable funds as depicted in the given graph, a change that increased the quantity people want to save at any given interest rate would cause a new equilibrium at a:
Considering the market for loanable funds as depicted in the given graph, a change that increased the quantity people want to save at any given interest rate would cause a new equilibrium at a:
A. higher interest rate and a lower equilibrium quantity of funds saved and invested. B. lower interest rate and a higher equilibrium quantity of funds saved and invested. C. higher interest rate and a higher equilibrium quantity of funds saved and invested. D. lower interest rate and a lower equilibrium quantity of funds saved and invested.