Which of the following is a component of the classical model?
a. Changes in aggregate demand cause movements along the long-run aggregate supply curve.
b. An increase in aggregate demand shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve rightward.
c. Changes in aggregate demand shift the long-run aggregate supply curve rightward.
d. An increase in aggregate demand quickly lowers the price level.
a. Changes in aggregate demand cause movements along the long-run aggregate supply curve.
You might also like to view...
The percentage change in quantity demanded of good A divided by the percentage change in price of good B is the formula for
a. cross-price elasticity of demand. b. income elasticity of demand. c. zero elasticity of demand. d. infinite elasticity of demand.
A forecaster used the regression equationQt = a + bt + c1D1 + c2D2 + c3D3and quarterly sales data for 1996 I - 2013 IV (t = 1, ..., 64) for an appliance manufacturer to obtain the results shown below. Q is quarterly sales, and D1, D2 and D3 are dummy variables for quarters I, II, and III.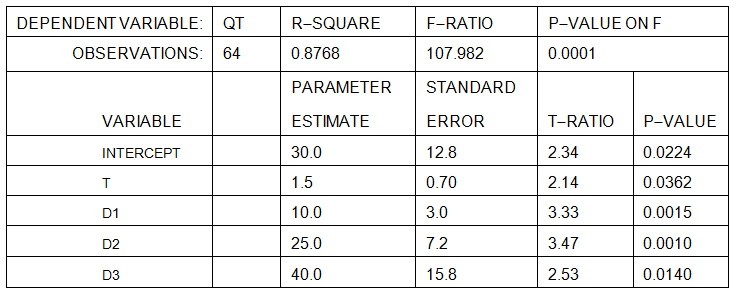 At the 5 percent level of significance, is there a statistically significant trend in sales?
At the 5 percent level of significance, is there a statistically significant trend in sales?
A. Yes, because 2.14 > 2.00. B. No, because 1.5 < 2.00. C. No, because 2.14 < 2.66. D. No, because 1.5 < 2.66. E. none of the above
If quantity demanded rises significantly following a moderate price cut, then demand is:
A. Elastic. B. Inelastic. C. Unitary elastic. D. Most likely elastic.
If a consumer is initially at an optimum, and then the price of Y decreases, then
A) MUX/PX > MUY/PY. B) MUX/PX < MUY/PY. C) MUX/PX = MUY/PY. D) MUX/MUY < PY/PX.