Refer to the table. Suppose that Libra decided to import more U.S. products. We would expect the quantity of libras:
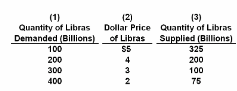
Answer the question on the basis of the following table, which indicates the dollar price of libras, the currency used in the hypothetical nation of Libra. Assume that a system of freely floating exchange rates is in place.
A. demanded at each dollar price to rise and the dollar to depreciate relative to the libra.
B. demanded at each dollar price to fall and the dollar to appreciate relative to the libra.
C. supplied at each dollar price to rise and the dollar to appreciate relative to the libra.
D. supplied at each dollar price to fall and the dollar to depreciate relative to the libra.
C. supplied at each dollar price to rise and the dollar to appreciate relative to the libra.
You might also like to view...
According to the shutdown rule, a firm should produce no output in the short run if
A) price is below minimum average total cost. B) price is above minimum average total cost. C) total revenues are lower than total fixed costs. D) price is below minimum average variable costs.
Suppose market demand is p = 10 - Q. Firms incur no cost of production. If firm A is the incumbent, can it deter the entry of its rival, firm B?
What will be an ideal response?
A study of expenditures on food in cities resulting in the following equation: Log E = 0.693 Log Y + 0.224 Log N where E is Food Expenditures; Y is total expenditures on goods and services; and N is the size of the family. This evidence implies:
a. that as total expenditures on goods and services rises, food expenditures falls. b. that a one-percent increase in family size increases food expenditures .693%. c. that a one-percent increase in family size increases food expenditures .224%. d. that a one-percent increase in total expenditures increases food expenditures 1%. e. that as family size increases, food expenditures go down.
A currency appreciation is disinflationary and contractionary if the
a. inward shift of the aggregate demand curve due to the fall in exports exceeds the outward shift of the aggregate supply curve due to lower input prices. b. outward shift of the aggregate demand curve due to the rise in exports exceeds the outward shift of the aggregate supply curve due to lower input prices. c. outward shift of the aggregate demand curve due to the fall in exports exceeds the inward shift of the aggregate supply curve due to higher input prices. d. inward shift of the aggregate demand curve due to lower input prices exceeds the outward shift of the aggregate supply curve due to the rise in exports.