Which of the following is a difference between "quantitative easing" and ordinary open-market operations?
A. There is no difference between the two policy tools.
B. Open-market operations are done in order to lower interest rates; quantitative easing is
merely intended to increase bank reserves.
C. Quantitative easing is focused exclusively on U.S. government bonds; open-market
operations also include the buying and selling of debt issued by government agencies and
government-sponsored entities.
B. Open-market operations are done in order to lower interest rates; quantitative easing is
merely intended to increase bank reserves.
You might also like to view...
Consider the following statement, "The Federal Reserve fights recessions by increasing the money supply so people will have more money to spend." What is wrong with the statement and how can it be corrected?
What will be an ideal response?
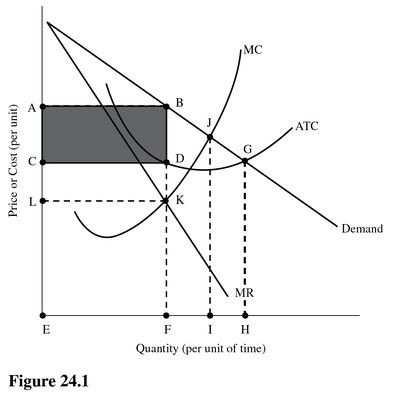 The profit-maximizing rate of output in Figure 24.1 is
The profit-maximizing rate of output in Figure 24.1 is
A. F. B. I. C. H. D. E.
A perfectly horizontal demand curve has
A. negative elasticity. B. some positive finite elasticity. C. zero elasticity. D. elasticity equals infinity.
Explain why even small changes in the rate of economic growth are significant. Use the “rule of 70” to demonstrate the point.
What will be an ideal response?