Using the figure below, identify the labeled items.
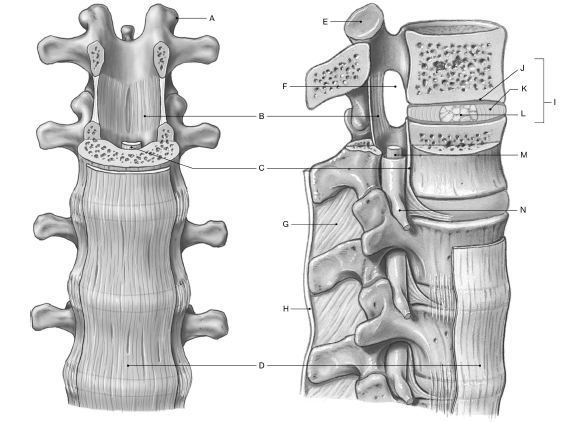
1) Label A: ______________________________
2) Label B: ______________________________
3) Label C: ______________________________
4) Label D: ______________________________
5) Label E: ______________________________
6) Label F: ______________________________
7) Label G: ______________________________
8) Label H: ______________________________
9) Label I: ______________________________
10) Label J: ______________________________
11) Label K: ______________________________
12) Label L: ______________________________
13) Label M: ______________________________
14) Label N: ______________________________
1) Superior articular process
2) Ligamentum flavum
3) Posterior longitudinal ligament
4) Anterior longitudinal ligament
5) Superior articular facet
6) Intervertebral foramen
7) Interspinous ligament
8) Supraspinous ligament
9) Intervertebral disc
10) End plate
11) Anulus fibrosus
12) Nucleus pulposus
13) Spinal cord
14) Spinal nerve
You might also like to view...
The phenotypes and genotypes that result from a cross of Aa and aa (A = normal pigmentation and a = albinism) are
A. phenotypes:all albino; genotypes:50% heterozygous and 50% homozygous recessive. B. phenotypes:all normal; genotypes:50% heterozygous and 50% homozygous recessive. C. phenotypes:all albino; genotypes:all homozygous recessive. D. phenotypes:50% normal and 50% albino; genotypes:50% heterozygous and 50% homozygous recessive.
Another name for the Haversian system is:
a. central canal b. lacunae c. canaliculi d. osteon
Muscle tissue has all of the following properties except ________
A) excitability B) extensibility C) contractility D) secretion
Incomplete tetanus
A. is the time during which the tissue cannot respond again. B. results in complete and incomplete tetanus. C. is the condition in which the muscle fiber only partially relaxes between contractions. D. is the condition in which stimuli occur so rapidly that there are no intervening relaxations. E. is the constant tension produced by muscles for long periods of time.