The price of a factor of production that is in fixed supply is called
A) opportunity cost. B) a compensating differential.
C) economic rent. D) economic profit.
C
You might also like to view...
Refer to the market diagram. Relative to the surplus they would receive in a competitive market, consumers lose how much surplus because there is a monopoly?
The following questions refer to the accompanying market diagram. PC and QC are the equilibrium price and quantity if the firm behaves competitively, and PM and QM are the equilibrium price and quantity if the firm is a simple monopoly.
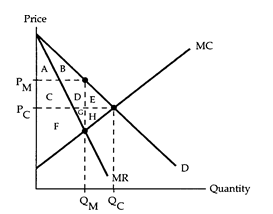
a. Area F + G + H
b. Area C + D + E
c. Area E + H
d. Area A + B
Which of the following properties is seen in a buy-sell transaction arranged by a pipeline?
a. Pipelines offer to resell gas to consumers even at a loss. b. Gas producers offer to sell gas to the pipelines at a discounted prices. c. Gas producers ration the amounts they supply to the pipelines. d. Pipelines evade the legal ceiling on their transportation charge by bundling the gas with transportation service.
Refer to Figure 9.1. At what price and quantity combination is profit maximized?
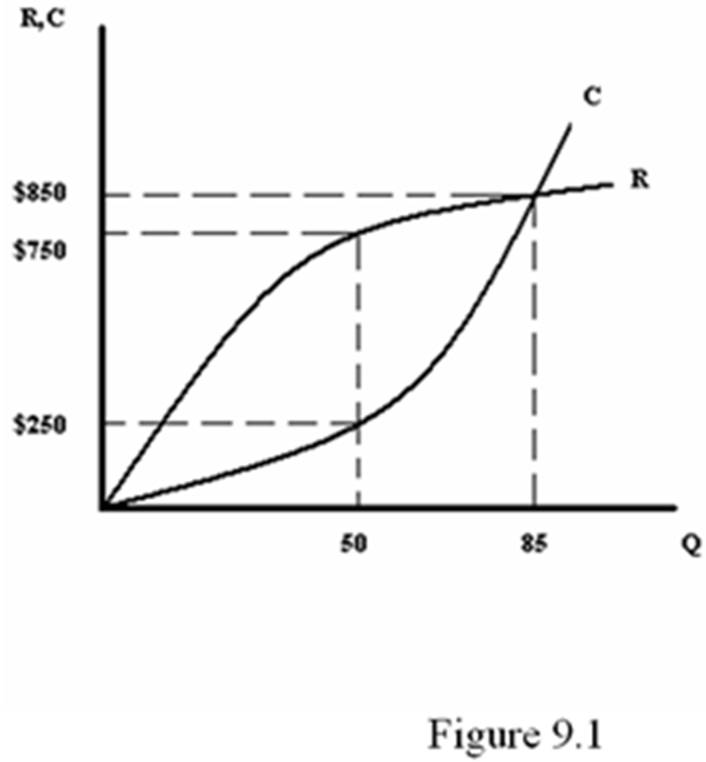
A. Q = 50; P = $5
B. Q = 50; P = $15
C. Q = 85; P = $10
D. Q = 85; P = $15
Explain what economists mean when they say that the United States is a net debtor nation. Identify a potential problem and a positive aspect associated with this status.
What will be an ideal response?