What was the solar neutrino problem?
What will be an ideal response?
Electron neutrinos coming from the Sun had been detected, but in fewer numbers than predicted by theoretical models. This meant either that our models of the Sun were wrong in some way (for example, we did not correctly predict the central temperature of the Sun) or, alternatively, that we did not understand neutrinos as well as we thought we did. The solar neutrino problem was solved by the Sudbury Neutrino Observatory (SNO) in Canada which used heavy water to detect all known types of neutrinos. SNO found that the electron neutrinos emitted in the core of the Sun can change into other types as they travel through the Sun explaining why fewer electron neutrinos are detected at the Earth.
You might also like to view...
Power: A battery supplies 6.0 mA to a 12-? resistor for 1.5 h. How much electric energy does this resistor dissipate in this time?
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
A squat refrigerator magnet sits on a table with its north pole facing up and its south pole down. We push a ring of wire lying on the table directly toward the magnet. What direction does current flow in the ring when viewed from above? (A wooden table will not affect the magnet’s field.)
A. Clockwise B. Counterclockwise C. No current flows in the loop.
A cylinder, semicircular in cross-section, 10.0 m long and 5.00 m in radius, is completely submerged in water. What is the buoyant force on the cylinder?
A) 1.92 × 106 N B) 3.85 × 106 N C) 5.78 × 106 N D) 6.28 × 106 N E) 7.70 × 106 N
A bar magnet is dropped from above and falls through the loop of wire shown below. The north pole of the bar magnet points downward towards the page as it falls. Which statement is correct?
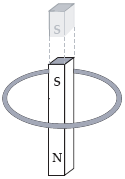
a.
The current in the loop always flows in a clockwise direction.
b.
The current in the loop always flows in a counterclockwise direction.
c.
The current in the loop flows first in a clockwise, then in a counterclockwise direction.
d.
The current in the loop flows first in a counterclockwise, then in a clockwise direction.
e.
No current flows in the loop because both ends of the magnet move through the loop.