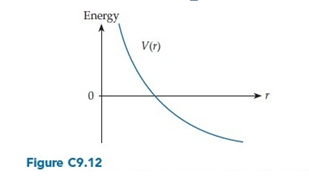
 Figure C9.12 shows the potential energy function for a certain interaction. This interaction is
Figure C9.12 shows the potential energy function for a certain interaction. This interaction is
A. Always attractive.
B. Always repulsive.
C. Attractive for small r, but repulsive for large r.
D. Repulsive for small r, but attractive for large r.
B. Always repulsive.
You might also like to view...
Where does the energy come from that your body uses to keep you alive?
A) It comes from the foods you eat. B) It is produced from the radiative energy of the Sun on your skin. C) It is created during the time that you rest or sleep. D) It comes from the water you drink. E) It is in the air that you breathe.
A blob of material in outer space moves at 3 m/s when it collides and sticks to a half-as-massive blob initially at rest. Compared with the initial kinetic energy of the 3-m/s blob, the kinetic energy of the coupled blobs is
A) one-third. B) two-thirds. C) three-quarters. D) not enough information
A pion is an unstable particle that has a mean lifetime of 2.55 × 10-8 s. This is the time interval between its creation in a nuclear process and its extinction into decay products,
as measured in a frame of reference at rest with respect to the pion. An average pion is traveling at 0.230c relative to Earth. How far does it travel in its lifetime, relative to Earth? A) 2.07 m B) 1.81 m C) 2.23 m D) 3.22 m E) 3.50 m
If the outside air pressure decreases, the reading on a tire gauge connected to a tire decreases
Indicate whether the statement is true or false