What is the problem with the argument that infant industries need to be protected from foreign competition?
What will be an ideal response?
Infant industry arguments rely on the idea that in industries with economies of scale, or substantial learning by doing, it is important for policymakers to protect local firms early in their development. One of the problems with this argument is that starting a company in isolation may deprive it of "technological spillovers" that its competitors, all located near one another, may enjoy—the isolated company will be the last to learn of changes in the industry.
You might also like to view...
The development of countries like South Korea has been supported by all of the following EXCEPT
A) high domestic interest rates. B) high domestic saving rates. C) large endowments of human capital. D) high levels of labor productivity. E) reduced government regulation.
The In the News article in the text titled "Fiscal Policy in the Great Depression" discusses fiscal spending and taxation. During the Great Depression, the federal government pursued a policy of fiscal restraint that led to
A. A decrease in aggregate demand. B. An increase in aggregate supply. C. A decrease of the federal deficit. D. The retirement of bonds, which reduced the federal debt.
Refer to Figure 7-12 An increase in price from $20 to $30 would
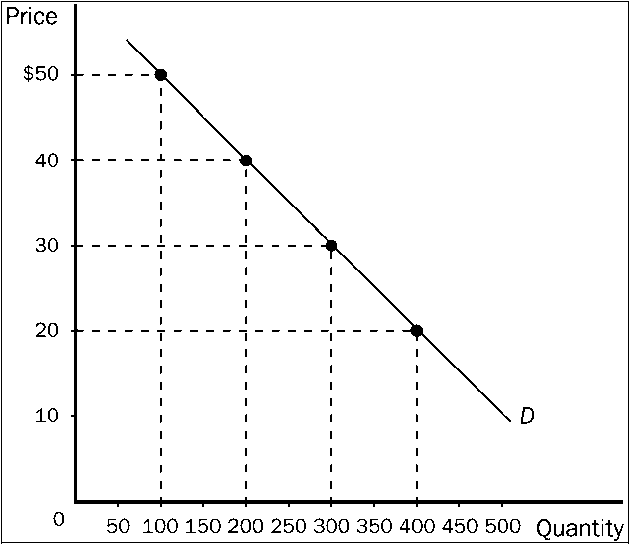
Refer to . An increase in price from $20 to $30 would
a.
increase total revenue by $2,000.
b.
decrease total revenue by $2,000.
c.
increase total revenue by $1,000.
d.
decrease total revenue by $1,000.
Both perfect competitors and monopolistic competitors
A. Earn zero economic profit in the long run. B. Find prices pushed to the minimum of long-run ATC by entry. C. Experience product differentiation. D. Use marginal cost pricing.