An individual or country that has a comparative advantage in the production of one good:
A. must have an absolute advantage in the good's production.
B. must not have an absolute advantage in the good's production.
C. may or may not have an absolute advantage in the good's production.
D. must not have an absolute advantage in the production of the other good.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Since World War II, the likelihood that foreign markets would gain importance to average exporters as a source of profits has
A) remained constant. B) increased. C) decreased. D) fluctuated widely with no clear trend. E) increased slightly before dropping off.
Farming in poor countries is considered to be:
A. capital intensive. B. labor intensive. C. production intensive. D. cost intensive.
The profit-maximizing firm will operate at an output of
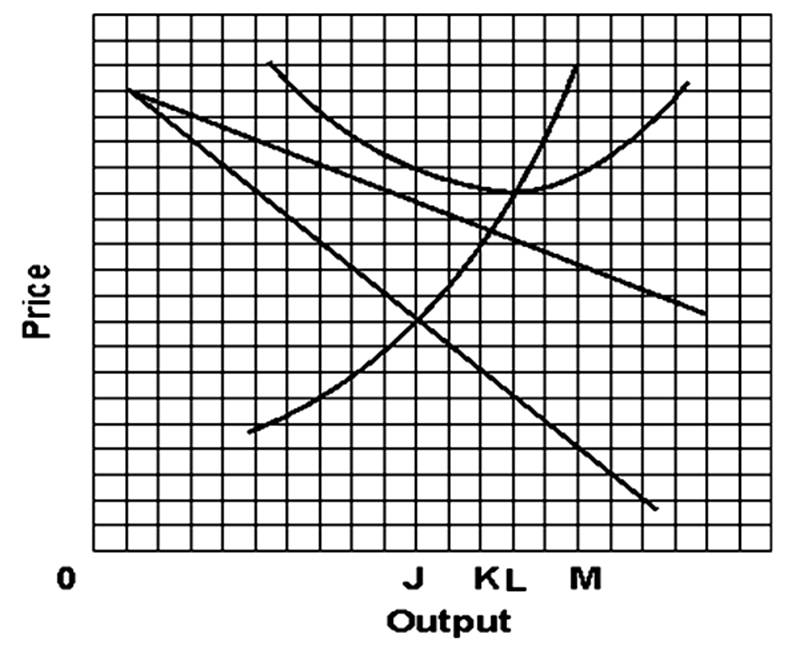
A. 0J.
B. 0K.
C. 0L.
D. 0M.
Consider a consumer who spends all income on only two goods: pizza and soda. An extra slice of pizza would give the consumer 60 extra utils, while an extra can of soda would give the consumer 20 extra utils. Pizza costs $3 per slice, and soda costs $1 per can. In this situation, the consumer:
A. is buying too much pizza and not enough soda. B. should purchase more pizza and less soda. C. has maximized his or her total utility. D. needs to equate the marginal utilities for pizza and soda.