Suppose the government of South Island fixes the exchange rate of its currency, the Islandia, in terms of the U.S. dollar. Initially the exchange rate is set at $1 per Islandia. In a crisis, the government changes the exchange rate to $0.50 per Islandia. This is an example of a(n):
A. revaluation.
B. devaluation.
C. appreciation.
D. depreciation.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
For a fixed proportion production function, at the vertex of any of the (L-shaped) isoquants the marginal productivity of either input is:
a. constant. b. zero. c. negative. d. a value that cannot be determined.
Someone who studies the pricing policies of the Microsoft Corporation would be a microeconomist.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Suppose the domestic supply (QS) and demand (QD) for skateboards in the United States is represented by the following set of equations:QS = -60 + 3PQD = 390 - 2PIf the United States can import skateboards from the rest of the world at a per unit price of $75, how many skateboards will be produced in the United States?
A. 285 B. 240 C. 165 D. 215
The economy pictured in the figure has a(n) ________ gap with a short-run equilibrium combination of inflation and output indicated by point ________. 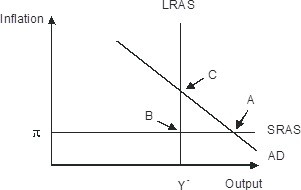
A. recessionary; A B. recessionary; C C. recessionary; B D. expansionary; A