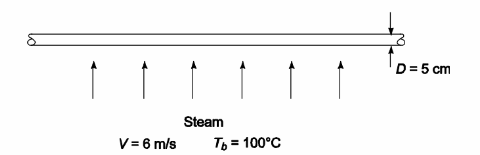
Steam at 1 atm and 100°C is flowing across a 5-cm-OD tube at a velocity of 6 m/s. Estimate the Nusselt number, the heat transfer coefficient, and the rate of heat transfer per meter length of pipe if the pipe is at 200°C.
GIVEN
• Steam flowing across a tube
• Steam pressure = 1 atm
• Steam bulk temperature (Tb) = 100°C
• Tube outside diameter (D) = 5 cm = 0.05 m
• Steam velocity (V) = 6 m/s
• Pipe surface temperature (Ts) 200°C
FIND
(a) The Nusselt number Nu D (b) The heat transfer coefficient h c(c) The rate of heat transfer per unit length (q/L)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0249 W/(m K) Kinematic viscosity (?) = 20.2 × 10–6 m2/s Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.987 At the tube surface temperature of 200°C, the Prandtl number of the steam (Prs) = 1.00
The Reynolds number is
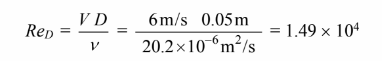
(a) The Nusselt number for this geometry is given by
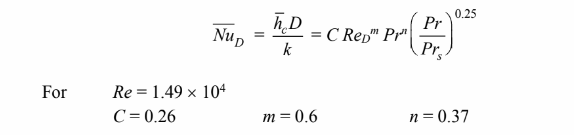
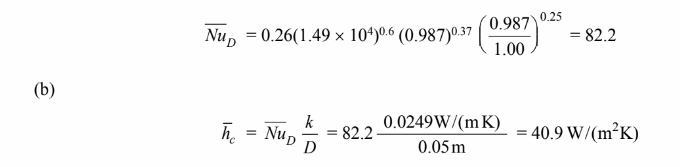
(c) The rate of heat transfer by convection from the tube is
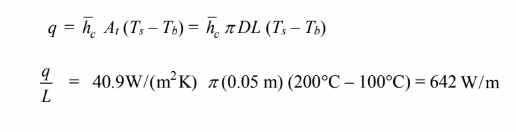
You might also like to view...
An object transfers heat when its temperature is raised by contact with a
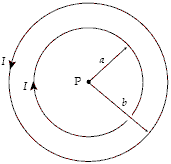
What is the magnitude of the magnetic field at point P in the figure if a = 2.0 cm, b = 4.5 cm, and I = 5.0 A?
a.
87 ?T, into the paper
b.
87 ?T, out of the paper
c.
0.23 mT, out of the paper
d.
0.23 mT, into the paper
e.
23 ?T, into the paper
Observations indicate that over billions of years, galaxies in general tend to change from
A) smaller and bluer to larger and redder. B) larger and redder to smaller and bluer. C) smaller and redder to larger and bluer. D) larger and bluer to smaller and redder.
In the absence of an external force, a moving object will
A) stop immediately. B) slow down and eventually come to a stop. C) gradually speed up until it reaches its terminal velocity. D) move with constant velocity in a straight line. E) move with constant velocity in a circular orbit.