Which of the following is the Fed's best strategy for dealing with demand shocks?
a. Maintain a money supply target
b. Decrease the money supply
c. Maintain a passive monetary policy
d. Neutralize the impact with an increase in the money supply
e. Increase the interest rate
D
You might also like to view...
Use the following graphs for a perfectly competitive market in the short run to answer the next question.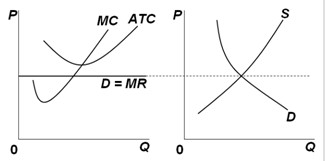 What will happen in the long run to market supply and the equilibrium price of the product?
What will happen in the long run to market supply and the equilibrium price of the product?
A. Market supply will increase and equilibrium price will increase. B. Market supply will decrease and equilibrium price will decrease. C. Market supply will decrease and equilibrium price will increase. D. Market supply will increase and equilibrium price will decrease.
The cost to firms of changing prices
A) is called a menu cost. B) is small even when there is rapid inflation. C) does not exist if inflation is perfectly anticipated. D) all of the above
Which is NOT an example of moral hazard
a. people eat more at all-you-can-eat buffets b. loggers select the most profitable trees to harvest even when they are paying a fixed fee c. Drivers of heavier, safer cares are more likely to run stop signs d. workers on commission work harder than those paid an hourly wage
The price elasticity of demand can be defined as ______.
a. the percentage change in price divided by the percentage change in quantity demanded b. the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price c. the percentage change in price multiplied by the percentage change in quantity demanded d. the percentage change in quantity demanded multiplied by the percentage change in price