A production possibilities curve that is a straight line represents the case of
A) constant costs.
B) increasing costs.
C) constant opportunity costs but increasing real costs.
D) constant opportunity costs but decreasing real costs.
A
You might also like to view...
When comparing perfect competition to a single-price monopoly with the same costs
A) both market types use resources efficiently. B) there is a deadweight loss associated with a monopoly. C) the sum of producer and consumer surplus is maximized under a monopoly. D) the sum of producer and consumer surplus is minimized under perfect competition.
The rate of return on bonds is lower than on stocks over time because
A) bond holders cannot diversify. B) bonds have a lower standard deviation in returns. C) stocks have less non-diversifiable risks than bonds. D) bonds are subject to more random risks than stocks.
According to the table shown, what is the firm's total revenue when 4 units are produced?
This table shows the total costs for various levels of output for a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market.
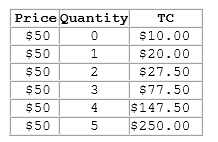
A. $160
B. $50
C. $200
D. $40
Which of the following is the velocity of money?
a. How quickly the average worker gets paid after his or her work is done. b. The average speed of ATM machines. c. The average number of times per year that a given dollar of the money supply is spent. d. None of the above.