Three policy lags limit the effectiveness of monetary policy: recognition lags, implementation lags, and impact lags. Of these three policy lags, fiscal policy is impacted by
A) only implementation and impact lags.
B) only recognition and implementation lags.
C) only recognition and impact lags.
D) all three policy lags.
D
You might also like to view...
Cap-and-trade refers to
A) capping emissions and issuing tradeable emissions permits. B) capping revenue from selling emissions permits. C) countries trading fishing rights in international waters. D) capping taxes on firms that engage in international trade. E) capping the benefits gained from pollution controls.
If an economy moves into a recession, causing that country to produce less than potential GDP, then:
a. automatic stabilizers will cause tax revenue to decrease and government spending to increase. b. automatic stabilizers will cause tax revenue to increase and government spending to decrease. c. tax revenue and government spending will be higher because of automatic stabilizers. d. tax revenue and government spending will be lower because of automatic stabilizers.
Congressman Smith and Congresswoman Johnson both consider themselves advocates for the national parks and are introducing different bills designed to benefit the parks. Congressman Smith's bill calls for an increase in the entrance fees. Congresswoman Johnson's bill calls for a decrease in the entrance fees. Which of the bills would be more effective at ensuring the quality of the national parks?
a. Congressman Smith's bill because it will reduce the overuse of the parks b. Congresswoman Johnson's bill because more visitors means more citizens will value and care for the parks c. Both bills would be equally effective. d. Neither bill would be effective.
Which of the following would most likely cause a shift to the right in Graph B?
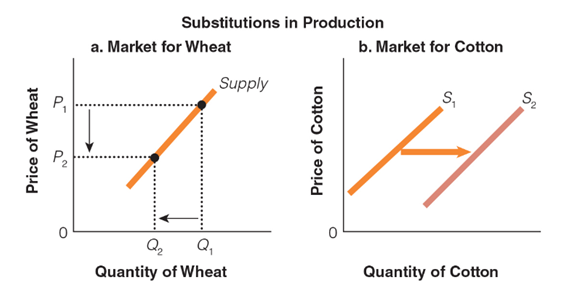
a. a change from Q1 to P1 in Graph A
b. a change from P2 to P1 in Graph A
c. a change from P1 to P2 in Graph A
d. a change from Q2 to Q1 in Graph A