A change in the price of a good causes
A) an increase in supply.
B) a decrease in supply.
C) an increase in demand and a decrease in supply.
D) a change in quantity supplied.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
If a decrease in price of good X causes the demand curve for good Y to increase, then these two goods are:
a. normal goods. b. complementary goods. c. substitute goods. d. equilibrium goods. e. market-day goods.
Suppose the central bank increases the money supply in an economy unexpectedly during a year. If the current inflation rate in this country is 3.4 percent, then according to new classical economists, the expected inflation rate for the following year would be:
a. 3.4 percent. b. less than 3.4 percent. c. 2.4 percent, because people form their expectations adaptively. d. around 6.8 percent. e. greater than 3.4 percent.
Productive efficiency means producing without:
a. cost. b. wages. c. waste. d. competition.
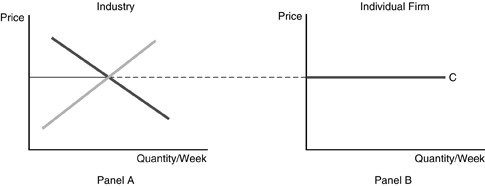 Refer to the above figure. Line C in Panel B does NOT represent
Refer to the above figure. Line C in Panel B does NOT represent
A. marginal revenue. B. total revenue. C. average revenue. D. the equilibrium price.