You are working in a laboratory that is studying a newly isolated virus. Your job is to culture the virus using in vitro methods. Upon observing your inoculated tissue culture specimen one day, you notice clumps of cells growing on top of the original monolayer of cells. Microscopic analysis of stained cells from the culture reveal an alteration in host cell membrane protein content and chromosomal structure. Based upon this information, you hypothesize that the virus you are studying is ________.
A. a viroid
B. an oncovirus
C. a bacteriophage
D. a prion
E. a satellite virus
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1.Gymnosperms are the flowering plants. 2.A seed is an embryo and its food supply is inside a seed coat. 3.The root and shoot apical meristems form at the same time in the plant embryo. 4.Seedless watermelons come from seeds that are triploid and therefore the seeds do not fully develop and form simple soft hulls that are easy to chew. 5.Coconuts are fruits containing seeds that are usually wind dispersed.
When a species lives in suitable habitats throughout a geographical area they have
1.disjunct distributions. 2.continuous distributions. 3.a dispersal. 4.a vicariance. 5.None of the options is correct.
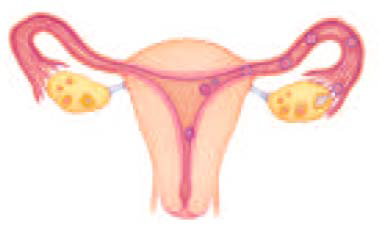
The accompanying figure illustrates the process of human development from fertilization to implantation. Describe what happens from day 1 through days 6-7 of this process
What factor(s) typically influence a trait that shows continuous variation?
A) genetic factors only B) environmental factors only C) both genetic and environmental factors D) neither genetic nor environmental factors