Which of the following situations results in a shortage of euros?
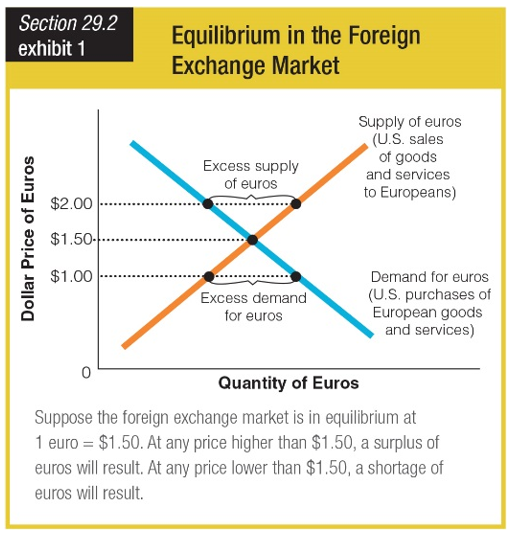
a. The dollar price of euros is much higher than $1.50.
b. The dollar price of euros is slightly higher than $1.50.
c. The dollar price of euros is equal to $1.50.
d. The dollar price of euros is less than $1.50.
d. The dollar price of euros is less than $1.50.
You might also like to view...
The output at which average variable cost is a minimum is ________ than the output at which ________ is a minimum
A) the same as; average total cost B) the same as; marginal cost C) less than; average total cost D) less than; marginal cost
Input efficiency:
A. means that holding constant the total amount of each input used in the economy, there is no way to increase any firm's output without decreasing the output of another firm. B. is not a requirement of Pareto efficiency in a production economy. C. exists when it is possible to produce more of one good and at least as much of every other good using the same inputs. D. is the same as efficient efficiency.
When consumers or businessmen stop collecting information to make decisions at the point where marginal cost of data collection equals the marginal utility of the data, economists would call the decisions based on existing data
A. perfect decisions. B. optimally imperfect decisions. C. joint decisions. D. rent seeking.
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
1. In the prisoners’ dilemma game, the prisoners can talk to each other about their decision. 2. The firms in an oligopoly often behave like the prisoners in the prisoners’ dilemma. 3. The arms race between the United States and the former Soviet Union is a classic example of the prisoners’ dilemma. 4. The tit-for-tat strategy is commonly used in one-shot games between oligopolists. 5. The snob effect is a positive network externality.