Microorg. are spread in hospitals through which route?
A. direct contact in contaminate food or intravenous solutions
B. indirect contact from patient to patient on the hands of health care workers
C. Inhalation of droplets
D. vector-borne contact
E. all of the above are correct
Ans: E. all of the above are correct
You might also like to view...
Trichomoniasis in humans is caused by a member of the ________ group of protists.
A. Parabasalia B. Amoebozoa C. Fornicata D. Euglenozoa
large granular leukocyte comprises ___% of circulating leukocytes
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following statements does not accurately describe the events involved in the propagation of an action potential?
(a) An initial influx of Na+ through a small cluster of channels causes local depolarization of the membrane. (b) Local depolarization causes nearby Na+ channels to open. (c) Channels in depolarized regions of the membrane are inactivated until the resting membrane potential is reestablished. (d) The opening of transmitter-gated K+ channels helps to repolarize the membrane.
Which of the following is an appropriate interpretation for these graphs?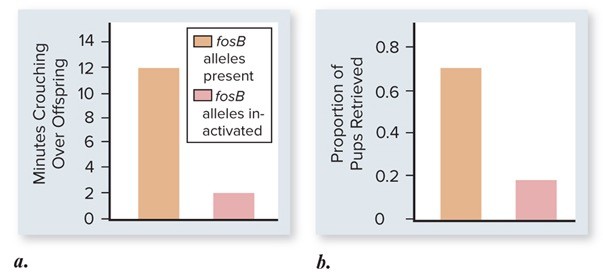 Maternal care (as measured by minutes crouching over offspring and proportion of pups retrieved) in female mice that have the fosB allele is
Maternal care (as measured by minutes crouching over offspring and proportion of pups retrieved) in female mice that have the fosB allele is
A. not possible to determine from the data. B. the same as the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele. C. less than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele; however, the graphs depict only minor differences, which are most likely not significant. D. less than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele. E. greater than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele.