Winogradsky columns ________.
A. are used in the process of isolating nanobacteria
B. are used in the process of isolating aquatic viruses (virioplankton)
C. are typically used to isolate aquatic protozoa
D. are used as a model system for studying microbial interactions
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Morgan's student Sturtevant demonstrated that the recombination frequencies between a series of linked genes is additive. Examine the following recombination data from Sturtevant, and determine the proper order of the genes on the Drosophila X chromosome. Assume y is in the 0.0 position.
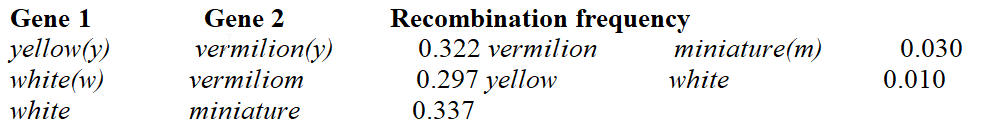
A. y m v w
B. y w v m
C. y m w v
D. y w m v
Clarify Question
· What is the key concept addressed by the question?
· What type of thinking is required?
· What key words does the question contain?
Gather Content
· What do you already know about recombination frequency?
Consider Possibilities
· What other information is related to the question? Which information is most useful?
Choose Answer
· Given what you now know, what information and/or problem solving approach is most likely to produce the correct answer?
Reflect on Process
· Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
The products of the C4 cycle
a. are immediately used in CAM plants. b. are stored by CAM plants in the central vacuole. c. are stored by CAM plants in the stroma. d. diffuse to bundle sheath cells for immediate use in C4 plants. e. are stored in mesophyll cells of C4 plants.
During which process are two diploid cells produced?
a. meiosis I b. meiosis II c. mitosis d. interphase
The enormous genetic diversity of HIV has made it especially difficult to create a vaccine against the virus. We can attribute this genetic diversity to
A. mutation hotspots in the hemagglutinin (H) molecule. B. the high error rate of reverse transcriptase. C. the high sensitivity of the virus to UV radiation. D. mutation hotspots in the CD4+ molecule.