Refer to Figure 6.5. By how many hours does leisure change as a result of the income effect of the wage change?
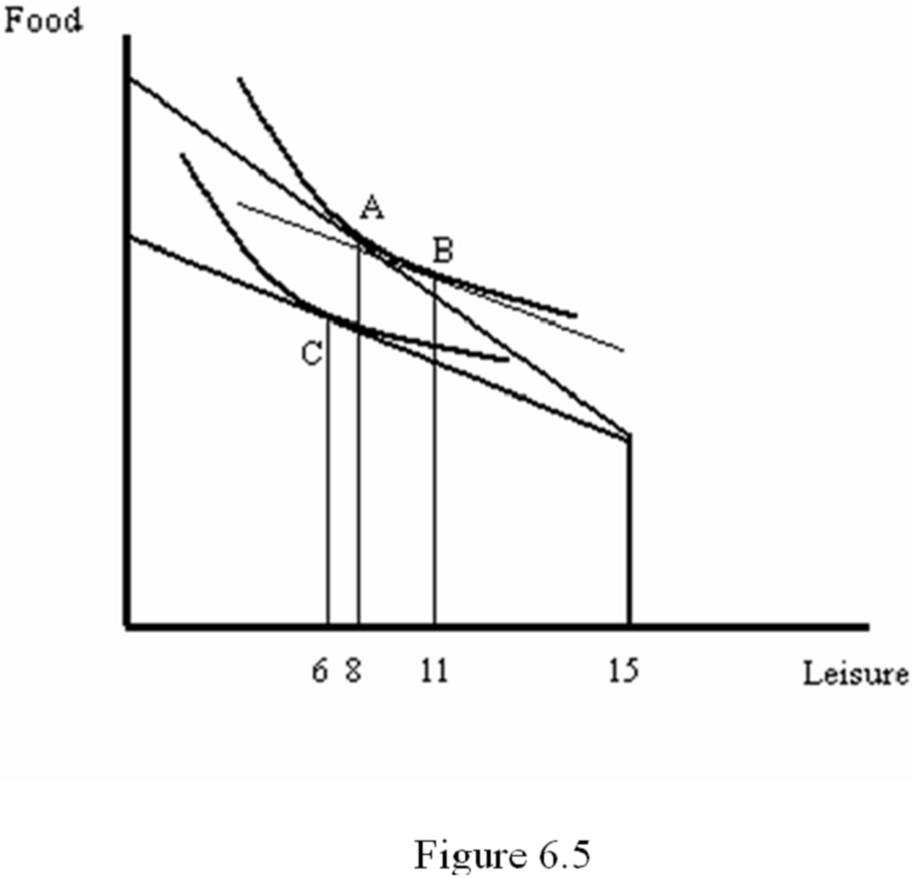
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
D. 5
You might also like to view...
The above figure shows the market for gourmet ice cream. In effort to reduce obesity, government places a $2 tax per gallon on suppliers in this market, shifting the supply curve from S0 to S1. The total tax revenue is equal to
A) $400,000. B) $800,000. C) $500,000. D) $200,000. E) More information is needed to determine the total tax revenue.
Jason hires Maria to tutor him in economics. Jason is willing to pay $30 for the first hour of tutoring, $25 for the second, $20 for the third, $15 for the fourth, and $10 for the fifth
Maria has an opportunity cost per hour of $6 for the first, $9 for the second, $12 for the third, $15 for the fourth, and $18 for the fifth. What will be the equilibrium quantity of hours tutored and the equilibrium price? Explain why this quantity and price is the equilibrium. What is Jason's consumer surplus and what is Maria's producer surplus?
Refer to Table 2-19. What is Wilma's opportunity cost of making a bench?
A) 3 statues B) 1/2 of a bench C) 1.3 statues D) 1/3 of a statue
The actual benefit of a government subsidy is determined primarily by
a. the elasticities of demand and supply. b. the legal (or statutory) assignment of the subsidy c. the number of exchanges that are made possible as a result of the subsidy. d. whether the subsidy is paid by cash or check.