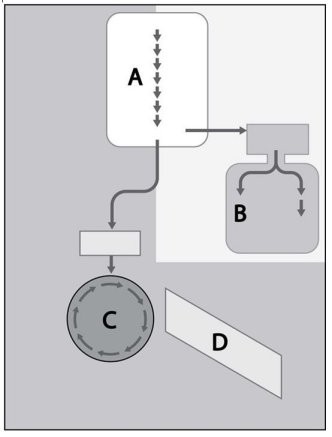
 Identify the processes of glucose metabolism represented in Figure 5.1.
Identify the processes of glucose metabolism represented in Figure 5.1.
A. A = electron transport chain, B = Citric acid cycle, C = glycolysis, D = fermentation
B. A = glycolysis, B = fermentation, C = Citric acid cycle, D = electron transport chain
C. A = fermentation, B = glycolysis, C = Citric acid cycle, D = electron transport chain
D. A = glycolysis, B = Citric acid cycle, C = fermentation, D = electron transport chain
E. A = glycolysis, B = Citric acid cycle, C = electron transport chain, D = fermentation
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Your instructor asks you to look into your microscope to see a prokaryotic cell. You will be looking for a cell that
A) has a nucleus. B) has a membrane. C) makes up most of the tissues of your body. D) is much larger than most cells in your body
Your grandmother has a rare disease for which a new genetic test has just been developed. If you are interested in a genetic test to determine whether you are affected, which of the following would you need to know to best interpret your test?
A. If you have one or two copies of a dominant allele B. Your father's genotype C. The penetrance of disease in people of your genotype D. The degree of variable expressivity if you lack a copy of the affected allele
In the sodium-potassium pump, sugars and amino acids, or other molecules, are brought through the membrane along with sodium ions through:
A. receptor proteins B. coupled channels C. chemiosmosis D. proton pumps
When molecules move through a cell membrane from an area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration by way of a channel protein, it is called:
A. endocytosis B. exocytosis C. facilitated diffusion D. osmosis E. simple diffusion