Nonexcludable goods tend to be undersupplied because:
A. the free rider problem persists.
B. people do not pay the true value of the good.
C. people rarely willingly pay for something they could get for free, regardless of how much they value it.
D. All of these statements are true.
D. All of these statements are true.
You might also like to view...
Describe the channels through which an open market purchase of bonds by the Fed affects output in a closed economy
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to the figure shown, which represents the production possibilities frontiers for Countries A and B. The slope of Country A's production possibilities frontier:
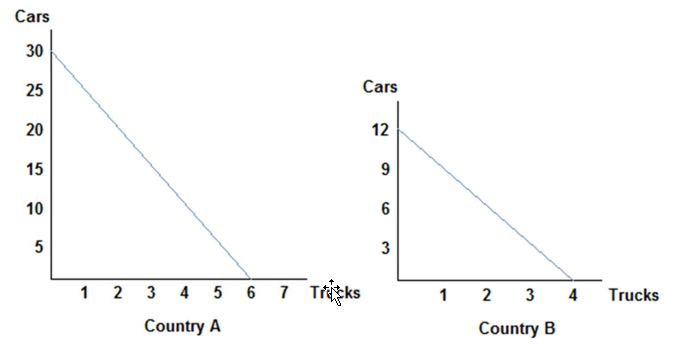
A. measures the opportunity cost of trucks in terms of cars.
B. measures the trade-off that Country A face when deciding how to allocate resources.
C. is constant because the opportunity cost remains constant.
D. All of these statements are true.
Real GDP is
A. nominal GDP adjusted for indirect business taxes. B. nominal GDP adjusted for price changes. C. nominal GDP adjusted for transfer payments. D. nominal GDP adjusted for depreciation.
If the price of a good rises by 10% and the percentage decrease in the total amount consumers spend on the good is 15%, then the good is
A. perfectly inelastic. B. unit elastic. C. elastic. D. inelastic.