The principal-agent problem arises in labor markets because:
A. a firm may realize excessively large profits.
B. workers may provide less-than-expected work effort.
C. compensating wage differences do not pay for differences in the nonmonetary aspects of
jobs.
D. human capital investments vary among workers.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
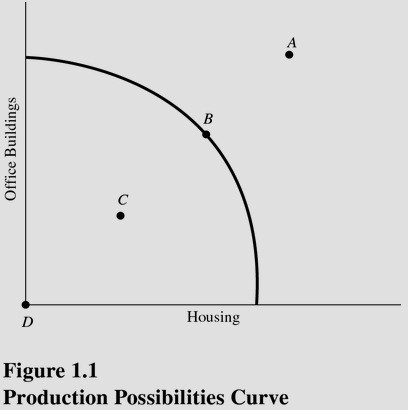 At which point is society producing some of each type of structure but still producing inefficiently? (See Figure 1.1.)
At which point is society producing some of each type of structure but still producing inefficiently? (See Figure 1.1.)
A. A. B. B. C. C. D. D.
(Last Word) "The government deregulated the electricity industry in California and a shortage of electricity soon occurred. It is clear that the deregulation caused the shortage." This statement needs careful analysis because it may reflect the:
A. fallacy of composition. B. post hoc, ergo propter hoc fallacy. C. use of loaded terminology. D. law of averages.
Hours of OperationMarginal Cost16212318424530636742 Krystal runs a nail salon and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Table 2.2 illustrates her marginal costs of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that we observe Krystal staying open 4 hours per day. If she is following the marginal principle, what must her marginal benefit be?
Krystal runs a nail salon and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Table 2.2 illustrates her marginal costs of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that we observe Krystal staying open 4 hours per day. If she is following the marginal principle, what must her marginal benefit be?
A. $12 B. $18 C. $24 D. $30
The amount of income received by households prior to the payment of personal income taxes is called
A. personal income. B. national income. C. net domestic product. D. disposable wages.