Refer to the diagram of the market for product X. Curve S t embodies all costs (including externalities) and D t embodies all benefits (including externalities) associated with the production and consumption of X. Assuming the equilibrium output is Q 2 ,
we can conclude that the existence of external:
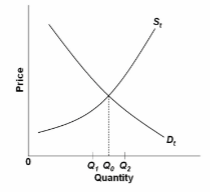
A. costs has resulted in an overallocation of resources to X.
B. benefits has resulted in an overallocation of resources to X.
C. costs has resulted in an underallocation of resources to X.
D. benefits has resulted in an underallocation of resources to X.
A. costs has resulted in an overallocation of resources to X.
You might also like to view...
Policy-oriented economists seek to develop theories to
A. explain how things work, so policies can be formulated. B. describe what happened in a particular time period in history. C. describe current economic events. D. find correlations between events. E. change people’s values and ethics.
According to this Application, workers in the EU were more productive than workers in Latvia in the 1990s, yet despite this, EU nations chose to trade with Latvia. Engaging in trade with Latvia allowed ________ to become more productive
A) workers in Latvia but not workers in the EU B) neither workers in the EU nor in Latvia C) workers in the EU but not workers in Latvia D) workers in both the EU and in Latvia
Gemma and Emily expect investments A and B to yield an annual return of 15 percent and 10 percent respectively. While Gemma invests in A, Emily invests in B. This implies that Gemma has a higher risk tolerance than Emily
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Which of the following is an example of an international externality?
a. Loss of crops b. Disease epidemic c. Global warming d. Dirty water