Perfectly competitive firms and monopolists are different because
a. in perfect competition MC = P, while a monopolist produces where P > MC.
b. in perfect competition MC = P, while a monopolist produces where MC > P.
c. in perfect competition P > MC, while a monopolist produces where MC = P.
d. in perfect competition MC > P, while a monopolist produces where MC = P.
a
You might also like to view...
Suppose you are the manager of a large cardboard box industry. In the industry, there are 10 very large firms and 15 small firms. You are aware that the very large firms have a greater marginal benefit from industrywide advertising compared to the small firms. Which of the following payment plans is least likely to create discord across the participating firms?
A) Have each firm pay the exact same fee. B) Have each firm pay the average marginal benefit of industrywide advertising across all firms. C) Place the very large firms into Group 1 and the small firms into Group 2 and require the firms in each respective group to pay the same amount with the firms in Group 1 paying a fee that is greater than the fee paid by Group 2 firms. D) Place the very large firms into Group 1 and the small firms into Group 2 and require the firms in each respective group to pay the same amount with the firms in Group 1 paying a fee that is smaller than the fee paid by Group 2 firms.
The meaning of interdependence in a monopolistically competitive market is
A) that it is difficult for firms to get together to collude. B) that products produced by firms will be good substitutes. C) that firms will not take into account the reaction of rival firms. D) that price rigging commonly occurs.
If the graph shown represents Stella's budget constraint, and she has income of $48 to spend on these two items, Stella could choose which consumption bundle?
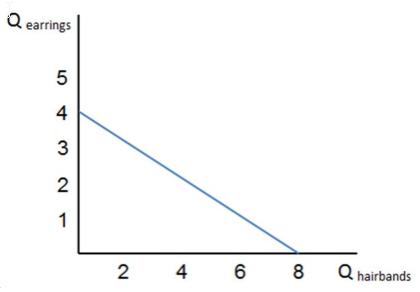
A. One pair of earrings and seven hairbands
B. Four pairs of earrings and eight hairbands
C. Three pairs of earrings and six hairbands
D. Two pairs of earrings and four hairbands
The price elasticity of demand measures the
a. responsiveness of a good's price to a change in quantity demanded b. adaptability of suppliers when a change in demand alters the price of a good c. responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in a good's price d. adaptability of buyers when there is a change in demand e. responsiveness of quantity supplied to a change in quantity demanded