Refer to Figure 20.2. Comparing the price elasticity of demand at points A and C, we can say that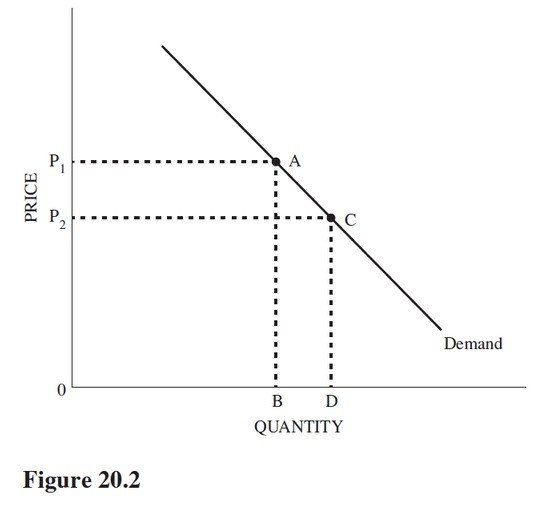
A. Point C has a greater price elasticity of demand in absolute value.
B. Demand elasticity is indeterminate because specific price data are not given.
C. The elasticities are the same because the points are on the same demand curve.
D. Point A has a greater price elasticity of demand in absolute value.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Which of the following could create a movement along the short-run Phillips curve so that the unemployment rate temporarily falls below the natural unemployment rate?
A) an increase in aggregate demand and a quickly responsive wage rate B) a decrease in aggregate demand and a sticky wage rate C) an increase in aggregate demand and a sticky wage rate D) an increase in aggregate supply and a sticky wage rate E) a decrease in aggregate demand and a quickly responsive wage rate
When two variables have a positive correlation,
a. they tend to move in opposite directions. b. they tend to move in the same direction. c. one variable will move while the other remains constant. d. the variables' values are never negative.
When deciding what price to charge consumers, the monopolist may choose to charge them different prices based on the customer's gender
a. true b. false
Consider a Cournot duopoly with the following inverse demand function: P = 100 ? 2Q1 ? 2Q2. The firms' marginal costs are identical and are given by MCi(Qi) = 2Qi. Based on this information, firm 1 and 2's reaction functions are:
A. r1(Q2) = 24.5 ? 0.5Q1 and r2(Q1) = 24.5 ? 0.5Q2. B. Q1 = 49 ? 0.25Q2 and Q2 = 49 ? 0.25Q1. C. r1(Q2) = 24.5 ? 0.5Q2 and r2(Q1) = 24.5 ? 0.5Q1. D. Q1 = 49 ? 0.5Q2 and Q2 = 49 ? 0.5Q1.