Which of the following would NOT affect a good's price elasticity of demand?
A) the ease of substitution between goods
B) the cost of producing the good
C) the number of substitute goods available
D) the proportion of one's budget spent on an item
B
You might also like to view...
The figure above shows the demand and cost curves for a single-price monopoly. The firm's economic profit equals
A) $0. B) $300. C) $100. D) $50.
Assume that the government increases spending and finances the expenditures by borrowing in the domestic capital markets. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a flexible exchange rate system, what happens to the quantity of real loanable funds per time period and the nominal value of the domestic currency in the context of the Three-Sector-Model?
a. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period rises, and nominal value of the domestic currency rises. b. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period falls, and nominal value of the domestic currency rises. c. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period rises, and nominal value of the domestic currency remains the same. d. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period rises, and nominal value of the domestic currency falls. e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.
The reason that differences in economic growth rates are important in the long run is that
A. real GDP usually drops when adjusted for inflation. B. population naturally shrinks in most countries. C. nominal GDP typically increases faster than real GDP. D. growth compounds over time.
Refer to the information provided in Table 21.6 below to answer the question(s) that follow. Table 21.6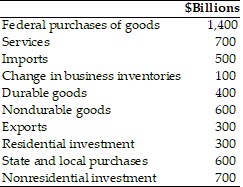 Refer to Table 21.6. The value for gross private domestic investment in billions of dollars is
Refer to Table 21.6. The value for gross private domestic investment in billions of dollars is
A. 800. B. 900. C. 1,000. D. 1,100.