Using the figure below, identify the labeled part.
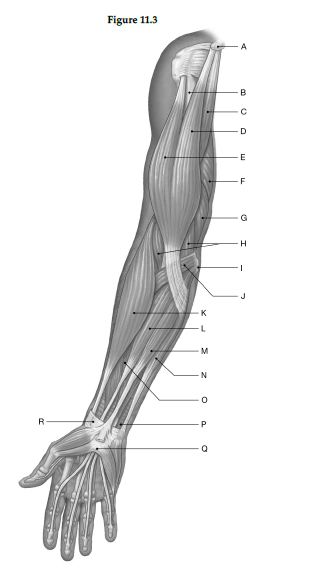
1) Label A: ______________________________
2) Label B: ______________________________
3) Label C: ______________________________
4) Label D: ______________________________
5) Label E: ______________________________
6) Label F: ______________________________
7) Label G: ______________________________
8) Label H: ______________________________
9) Label I: ______________________________
10) Label J: ______________________________
11) Label K: ______________________________
12) Label L: ______________________________
13) Label M: ______________________________
14) Label N: ______________________________
15) Label O: ______________________________
16) Label P: ______________________________
17) Label Q: ______________________________
18) Label R: ______________________________
1) Coracoid process of scapula
2) Humerus
3) Coracobrachialis
4) Biceps brachii, short head
5) Biceps brachii, long head
6) Triceps brachii, long head
7) Triceps brachii, medial head
8) Brachialis
9) Medial epicondyle of humerus
10) Pronator teres
11) Brachioradialis
12) Flexor carpi radialis
13) Palmaris longus
14) Flexor carpi ulnaris
15) Flexor digitorum superficialis
16) Pronator quadratus
17) Flexor retinaculum
18) Palmar carpal ligament
You might also like to view...
Adolescence begins at the period of sexual maturity called
A) menopause. B) puberty. C) senescence. D) postnatal. E) gestation.
A reduction in sensitivity to a continually applied stimulus is called
A. sensation. B. tonicity. C. conscious awareness. D. adaptation. E. transduction.
IgA is primarily found
A. in blood. B. in external secretions such as tears, saliva, and mucus. C. in lymph. D. on the surface of B-lymphocytes. E. in the thymus, spleen, and lymph nodes.
Which of the following is NOT an effector controlled by the autonomic nervous system?
A. Cardiac muscle B. Skeletal muscle C. Smooth muscle in the digestive system D. Smooth muscle in blood vessels E. Glands