A pool ball moving at 3 m/s collides head-on with an identical pool ball that's initially at rest. Just after the collision, the second ball moves away at 2 m/s while the first ball
A) moves at 3 m/s in a direction opposite to the second ball.
B) continues moving at 3 m/s in the same direction.
C) is at rest.
D) moves at 1 m/s in the same direction as the second ball.
E) moves at 1 m/s in a direction opposite to the second ball.
D
You might also like to view...
What is the mass of exactly 1 million helium atoms? The atomic mass of helium is 4.00 u.
A. 
B. 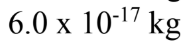
C. 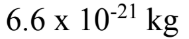
D. 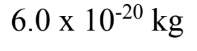
The figure below shows a planet traveling in a clockwise direction on an elliptical path around a star located at one focus of the ellipse. When the planet is at point A,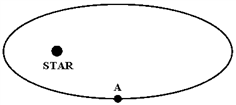
A. its speed is constant. B. its speed is increasing. C. its speed is decreasing. D. its speed is a maximum. E. its speed is a minimum.
The processes responsible for virtually all surface geology are ________
A) accretion, differentiation, and radioactive decay B) impact cratering, volcanisms, tectonics, and erosion C) convection, conduction, and radiation D) eruptions, lava flows, and outgassing
Briefly summarize current knowledge about the term NHP in the equation
Number of Civilizations = NHP × flife × fcivilization × fnow. What will be an ideal response?