Why are short-term solutions often offered to achieve sustainability? Why must sustainable solutions work in the long term? Why does the current political system inhibit our ability as a community to work on long-term solutions, and how can citizens
change this?
Policymakers in democracies very often act for short-term good because in order to be reelected, they need to produce immediate, positive results. This has been a major hurdle for addressing environmental dilemmas, since so many are cumulative problems that gradually worsen and can be resolved only in the long term. Often the best long-term solution is not the best short-term solution, a fact that explains why much of what human societies presently do is not sustainable. The costs for addressing environmental problems are often short-term while the benefits are long-term, giving politicians little incentive to tackle the issues. For this reason, pressure on policymakers by groups with heavy citizen involvement, such as conservation organizations like the Audubon Society or an environmental nongovernmental organization such as the National Resource Defense Council, is important for issues that involve long-term effects.
You might also like to view...
What is being depicted by this figure?
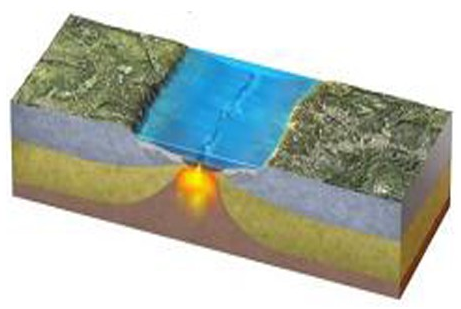
A) Continental collision
B) Continent-continent convergence
C) Early stages of seafloor spreading
D) Early stages of subduction
E) A boundary that is mostly a transform fault
Streams preferentially erode ________ and ________ valleys where rock is most easily eroded
A) deep, wide B) deep, narrow C) shallow, wide D) shallow, narrow
Imagine two hypothetical cities, both located at 12° N. However, one is located near sea level, while the other at an elevation of 4,000 m (13,123 ft) above sea level. Which of the following is likely true?
A) The city at the higher elevation has both average monthly and yearly temperatures lower than the city near sea level. B) Annual temperatures for the city at the lower elevation are lower than those at the city at the higher elevation. C) The climate of the two cities are quite similar. D) The city at the higher elevation will have warmer summers, but colder winters than the city at the lower elevation. E) The city at the higher elevation has extremely cold winters (similar to those at high latitudes)
The climates of the United States and Canada include the __________________ climate.
-desert Type B -tropical Type A -seasonal continental Type D -moderate/humid Type C -all of these are found in the region