Using the ZZ/Y and NX graphs, illustrate graphically and explain what effect a reduction in foreign output (Y*) will have on output, exports, imports, and net exports. Clearly label all curves and clearly label the initial and final equilibria
What will be an ideal response?
A reduction in foreign income, Y*, will cause a decrease in exports (the NX curve shifts up) and an decrease in demand. As demand falls, Y will decrease causing a fall in C and S. As Y decreases, imports will decrease as well. As shown in the text, the decrease in imports will be less than the fall in exports. So, NX will be lower.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as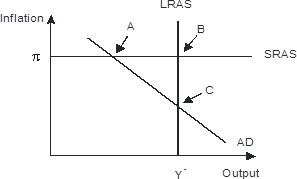
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward C. Aggregate demand shifting rightward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
During the 1930s, labor legislation was
(a) generally favorable to organized labor. (b) generally unfavorable to organized labor. (c) generally neutral with regard to organized labor. (d) virtually the same compared to previous periods.
The largest source of income for the federal government is
a. individual income taxes. b. corporate taxes. c. tariffs. d. "sin" taxes on alcohol and cigarettes.
A fall in the price of foreign inputs leads to a
A) rightward shift of the AD curve. B) leftward shift of the AD curve. C) rightward shift of the SRAS curve. D) leftward shift of the SRAS curve.