The age-earnings cycle is an earnings profile of an individual throughout the person's lifetime. The profile shows that
A. earnings usually peak at age 25 and then decline.
B. earnings and age have no particular correlation.
C. younger workers have the most productivity.
D. earnings gradually rise until they peak around age 50.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
In the early days of U.S. unionization, the Knights of Labor tried to
a. form unions that represented all workers in a single occupation b. form unions that represented all workers in a single industry c. organize labor across all skills, all industries, and all regions d. give broad representation to less-skilled industrial workers e. fight racial and sexual discrimination in the labor markets
Mutual funds
a. provide diversification. Shareholders assume all of the risk associated with the mutual fund. b. provide diversification. Government insurance eliminates the risk of mutual fund shareholders. c. do not provide diversification. Shareholders assume all of the risk associated with the mutual fund d. do not provide diversification. Government insurance eliminates the risk of mutual fund shareholders.
Suppose the Fed conducts an open market sale of $50 million in government securities. If the required reserve ratio is 20%, what is the maximum change in the money supply? Assume that banks try not to hold excess reserves and there is no currency withdrawal from the banking system.
A) maximum increase in money supply = $250 million B) maximum decrease in money supply = $250 million C) maximum increase in money supply = $50 million D) maximum decrease in money supply = $50 million
Exhibit 4-2 Supply and demand curves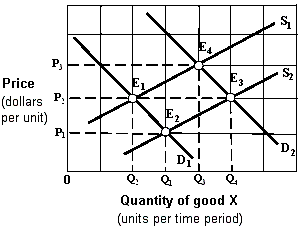
A. increase in demand and an increase in supply. B. decrease in demand and a decrease in quantity supplied. C. increase in supply and an increase in quantity demanded. D. decrease in supply and a decrease in quantity demanded.