Refer to Figure 7-16. Producer surplus amounts to $300 if the price of the good is
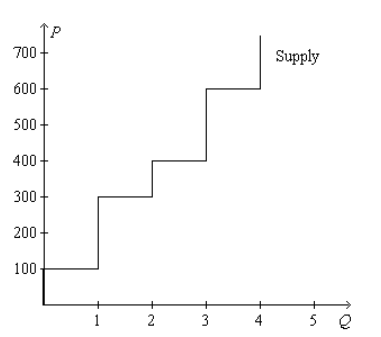
a. $300
b. $350
c. $400
d. $450
Answer: c. $400
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is a reason why the Consumer Price Index (CPI) is not calculated as a simple average of all prices?
a. Some goods experience large price changes and the CPI would be too variable if computed by a simple average. b. Goods differ in their importance in the average consumer's budget. c. Some goods never experience price changes and the CPI would not be variable enough if computed as a simple average. d. It would be difficult to compute a price index using a simple average of all prices. e. Actually, the CPI is a simple average of all prices.
A decrease in the money supply
a. lowers the interest rate, causing a decrease in investment and a decrease in GDP b. lowers the interest rate, causing a decrease in investment and an increase in GDP c. raises the interest rate, causing an increase in investment and a decrease in GDP d. raises the interest rate, causing an increase in investment and an increase in GDP e. raises the interest rate, causing a decrease in investment and a decrease in GDP
Which of the following is true?
A. The completion of the transcontinental railroad system in the 1880s eventually made the United States the world's first mass market. B. Southern manufacturers benefited from high protective tariffs of the 19th century that kept out cheaper Japanese manufactured goods. C. The canal system linking east-coast rivers with the Great Lakes in the 1820s created an "American economy" rather than just a series of regional economies located in one country. D. Agricultural inventions such as John Deere's steel plows did little to improve farm productivity.
Workers expect inflation to fall from 4% to 1% next year. As a result, this should
A) shift the short-run aggregate supply curve to the left. B) shift the short-run aggregate supply curve to the right. C) move the economy up along a stationary short-run aggregate supply curve. D) move the economy down along a stationary short-run aggregate supply curve.