Endochondral ossification ________, whereas intramembranous ossification ________.
A. forms bone in broad, flat areas of the skull; occurs in the limbs
B. inhibits osteoblast activity; activates osteoclast activity
C. activates osteoclasts; inhibits osteoblast activity
D. replaces hyaline cartilage; replaces undifferentiated connective tissue
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Bone is a connective tissue that provides support for the body with its strength and rigidity. Which of the following provides the best explanation for how this is so?
A) Bone cells are very dense and therefore resist physical stress. B) Bones cells secrete an extracellular matrix that when combined with minerals becomes rock hard. C) Bone cells have extensive cytoskeleton that makes them ridged. D) The bone cell's plasma membrane contains a high degree of cholesterol that stabilizes the cell membrane, giving it strength.
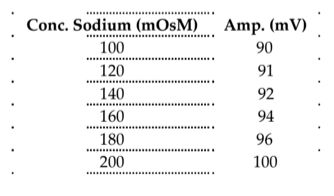
The amplitude of an action potential depends in part on the amount of sodium in the extracellular fluid. Stanley Student has carefully impaled a neuron with an intracellular electrode. He tests the role of extracellular sodium by changing the concentration in the bathing fluid and recording an action potential after each change. The data he generated are shown in the table, where amplitude listed
is the peak amplitude of the action potential; make an appropriate graph.
List two symptoms of equine infectious anemia
What will be an ideal response?
Sympathetic stimulation ____ heart rate and ____ the motility in the digestive tract
a. does not affect, decreases. b. decreases, decreases. c. decreases, increases. d. increases, decreases. e. increases, increases.