A frozen-food company freezes its spinach by first compressing it into large slabs and then exposing the slab of spinach to a low-temperature cooling medium. The large slab of compressed spinach is initially at a uniform temperature of 21°C; it must be reduced to an average temperature over the entire slab of –34°C. The temperature at any part of the slab, however, must never drop below –51°C. The cooling medium which passes across both sides of the slab is at a constant temperature of –90°C. The following data may be used for the spinach: density = 80 kg/m3; thermal conductivity = 0.87 W/(m K); specific heat = 2100 J/(kg K). Present a detailed analysis outlining a method estimate the maximum thickness of the slab of spinach that can be safely cooled in 60 min.
GIVEN
• Large slabs of spinach are exposed to a low-temperature cooling medium
• Initial uniform temperature (To) = 21°C
• Average temperature must be reduced to –34°C
• The temperature at any part must never drop below –51°C
• Cooling medium temperature (T?) = –90°C
• Density of spinach (?) = 80 kg/m3
• Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.87 W/(m K)
• Specific heat (c) = 2100 J/(kg K)
FIND
• Present a detailed analysis outlining a method to estimate the maximum thickness of the slab of spinach that can be safely cooled in 60 min
ASSUMPTIONS
• One dimensional conduction through the slab
• Constant and uniform thermal
properties
• The average temperature within the slab is equal to the average of the center and surface temperatures
SKETCH
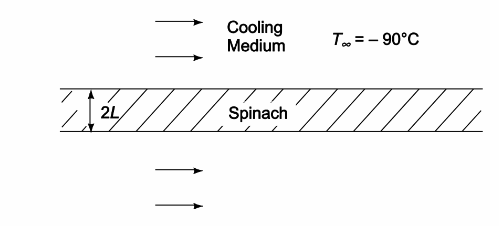
The average temperature for a slab with constant thermal conductivity is arithmetic average of center and end temperature. Thus, for a final average temperature in the slab of –34°C, and a final surface temperature of –51°C, the final center temperature must be
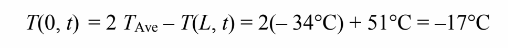
can be used to find the Biot number for the spinach slab
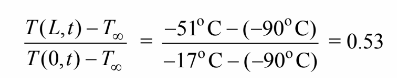
can be used to find the Fourier number

using above information, Fo = 0.5
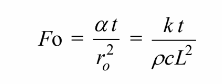
Solving for L
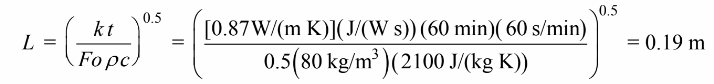
The thickness of the slab of spinach that can be cooled in 60 minutes is 2L = 0.38 m = 38 cm.
The heat transfer coefficient needed to achieve this cooling can be calculated from the Biot number
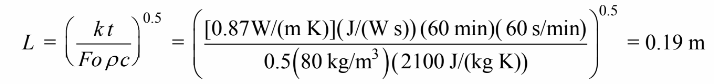
The approximate solution for slab of infinite length is given by.
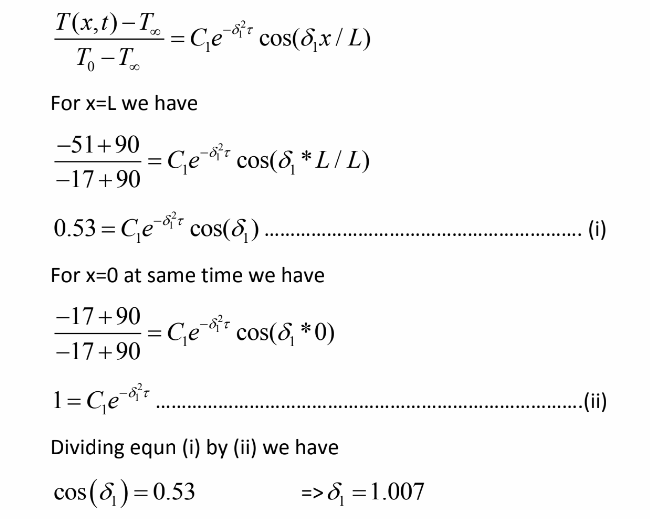
Dividing equn (i) by (ii) we have

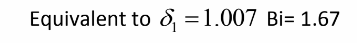
For infinite slab with Bi=1.67 we have
for x= 0, we have

Solving for L
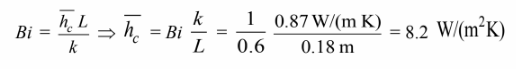
You might also like to view...
Two identical resistors are connected in series across the terminals of a battery with a voltage V and a current i flows through the circuit. If one of the resistors is removed from the circuit and the remaining one connected across the terminals of the battery, how much current would flow through the circuit?
a) 4i b) 2i c) i d) i/2
Light with a wavelength of 310 nm is incident on a metal that has a work function of 3.8 eV. What is the maximum kinetic energy that a photoelectron ejected in this process can have?
A) 0.62 × 10-19 J B) 0.21 × 10-19 J C) 0.36 × 10-19 J D) 0.48 × 10-19 J E) 0.33 × 10-19 J
When gas in a container expands to three times its volume at constant temperature, the gas pressure
A) is one third. B) is one ninth. C) triples. D) remains the same.
The percentage by mass of carbon in diamond is about
a. 25%. b. 75%. c. 100%. d. 20%.