Which of the following would be least likely to cause the production possibilities curve to shift outward?
a. a decreased desire for leisure by workers in the economy.
b. an invention that requires fewer resources to produce a good.
c. a shift in consumer preferences that causes expansion in the output of one product and a decline in output of other products.
d. an expansion in the man-made productive resources available to the economy as the result of a high rate of investment.
c
You might also like to view...
If the wage rate rises, then the firm's long-run marginal costs change, which in turn affects the firm's output level and its employment of labor. This phenomenon is known as
a. the substitution effect. b. the scale effect. c. the regressive-factor effect. d. the factor-price effect.
A demand schedule
A) shows that demand is on schedule. B) is a graph showing a relationship between the quantity demanded and the price of a good. C) shows the quantity demanded at one price. D) is a list of the quantities demanded at each different price when all other influences on buying plans remain the same. E) shows how the demand changes when the supply changes.
A physician's office expenses increase by 10 percent, so the doctor decides to raise the price of office visits. Assuming the demand curve for office visits does not shift, what will happen to the total number of office visits and practice revenues?
a. Office visits and total revenue rise if demand is inelastic. b. Office visits and total revenue stay the same if demand is elastic. c. Office visits will fall and total revenue will rise if demand is inelastic. d. Office visits will rise and total revenue will fall if demand is elastic. e. Office visits and total revenue fall if demand is inelastic.
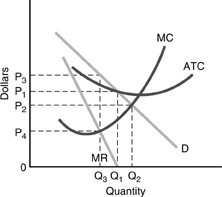 Use the above figure. The profit-maximizing price will be
Use the above figure. The profit-maximizing price will be
A. P1. B. P2. C. P3. D. P4.