In consumer equilibrium, the marginal utility of good A, B and C are 100, 300, and 400 respectively. If the price of good A was $35, then the prices of goods B and C, respectively, are:
a. $105 and $140.
b. $140 and $105.
c. $105 and $175.
d. $140 and $175.
a
You might also like to view...
If the economy were producing at point A and moved to point B the opportunity cost in terms of lost production of robots would be
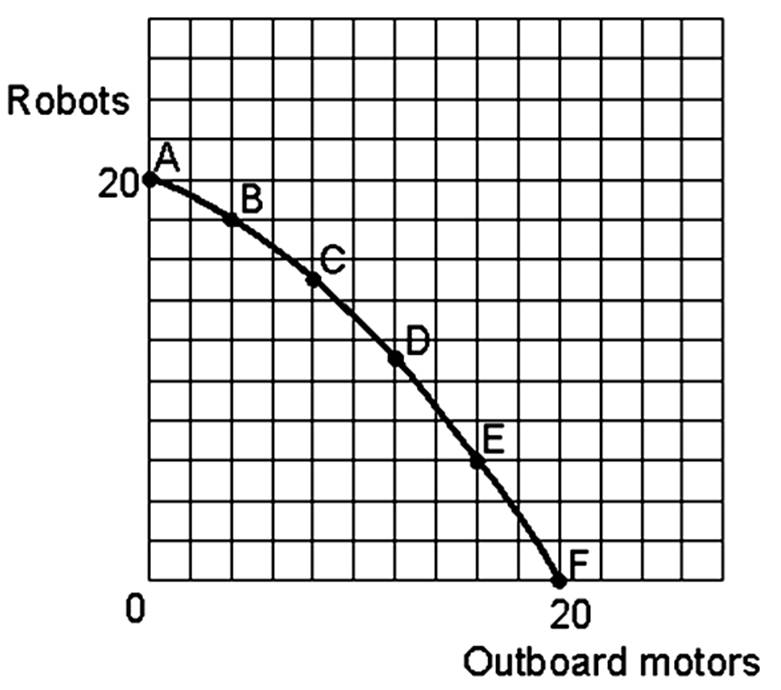
A. 1 unit of robots.
B. 2 units of robots.
C. 3 units of robots.
D. 2 units of outboard motors.
Refer to Table 2-5. What is Estonia's opportunity cost of producing one cell phone?
A) 0.2 board feet of lumber B) 5 board feet of lumber C) 8 board feet of lumber D) 32 board feet of lumber
If an economy produces 1,000 units of output with a price level of $5 and the money supply (M) is $1,000, velocity is:
A. 5. B. 200. C. 50. D. 2.
A binding price floor is: a. set with the aim of increasing the consumer surplus. b. set at the equilibrium price level
c. set below the equilibrium price level. d. set above the equilibrium price level.