External benefits are the extra
A) benefits a consumer gets from consuming a good.
B) costs a producer creates in producing a good.
C) benefits that accrue to people other than the consumers.
D) costs a producer bears for producing a polluting good.
E) benefits a producer obtains for reducing production of a polluting good.
C
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below.________ inflation will eventually move the economy pictured in the diagram from short-run equilibrium at point ________ to long-run equilibrium at point ________, 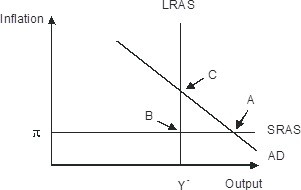
A. Rising; B; C B. Falling; A; C C. Falling; A; B D. Rising; A; C
The price paid by a tenant to rent an apartment most closely reflects the cost to the
A) landlord of constructing (or purchasing), maintaining, and operating the apartment. B) landlord of not renting to someone else. C) society of the opportunities thereby forgone. D) tenant of finding an alternative place to live.
In theory, differences in output across economies and over time might be the result of differences in either capital input, labor input, or productivity
The evidence points clearly to productivity as a more likely and powerful source of growth differences. Which aspects of the Solow growth model help to explain why the inputs of capital and labor contribute little to growth of output, relative to productivity?
Which of the following statements is correct?
a. The financial assets in M1 and M2 can be stored but not spent. b. All the financial assets in M1 can be spent. c. All the financial assets in M2 can be spent. d. All the financial assets in M1 and M2 can be spent. e. The financial assets in M2 are more liquid than the ones in M1.