The perfectly competitive firm's marginal revenue curve is
A) exactly the same as the marginal cost curve.
B) downward-sloping, at twice the (negative) slope of the market demand curve.
C) vertical.
D) horizontal.
E) upward-sloping.
D
You might also like to view...
Appendix: In regression analysis, the existence of a high degree of intercorrelation among some or all of the explanatory variables in the regression equation constitutes:
a. autocorrelation b. a simultaneous equation relationship c. nonlinearities d. heteroscedasticity e. multicollinearity
According to the graph shown, producing 14 units:
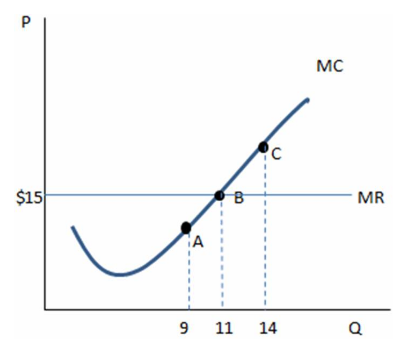
A. is not as profitable as producing 11 units.
B. will earn negative profits.
C. will earn more profits than producing 9 or 11 units.
D. will earn zero profit.
When a consumer is purchasing the best combination of two goods, X and Y, subject to a budget constraint, we say that the consumer is at an optimal choice point. A graph of an optimal choice point shows that it occurs
a. along the highest attainable indifference curve. b. where the indifference curve is tangent to the budget constraint. c. where the marginal utility per dollar spent is the same for both X and Y. d. All of the above are correct.
When marginal utility is negative, total utility
A. increases at a decreasing rate. B. is at its maximum. C. decreases. D. is zero.