Current and Capital Accounts
The Current Account - the balance of trade, the value of a nation’s imports subtracted from its exports. This measures the trade of goods and services.
The Capital Account - records the flow of payments for financial capital such as real estate, corporate stocks, bonds, government securities, and other debt instruments
- Deficits from the current account are funded from the capital account, so when a nation runs a deficit in the current account, it simultaneously runs a surplus in the capital account.
You might also like to view...
An outside lag is
A) a policy aimed at increasing GDP. B) a policy aimed at reducing GDP. C) a lag in implementing policy. D) the period of time it takes for policies to work.
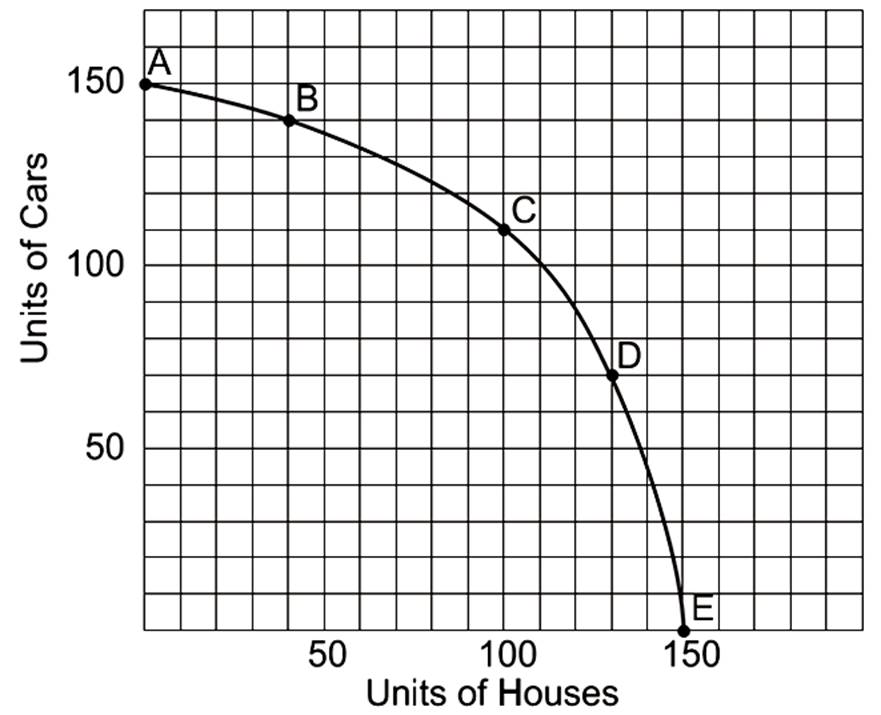
What is the opportunity cost of going from point D to point C?
A new firm successfully enters a three-firm Cournot oligopoly without changing the demand and cost structures. The new price becomes:
A. unknown for lack of other information. B. 50 percent of the original price. C. 75 percent of the original price. D. the same as the original price.
The equilibrium quantity is
A. always less than the equilibrium price. B. an amount lower than producers want to sell. C. an amount higher than consumers want to buy. D. the amount exchanged at the equilibrium price.