A situation where limited resources make it impossible to fulfill all of our wants is known as
A) scarcity.
B) opportunity cost.
C) a trade-off.
D) responding to incentives.
A
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as 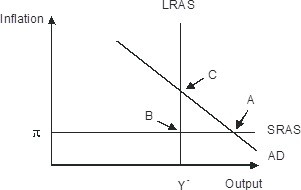
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting upward C. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
The figure above shows the U.S. demand and U.S. supply curves for cherries. In the absence of international trade, cherry farmers would receive ________ per pound of cherries
A) $2.50 B) $1.50 C) $2.00 D) $1.00 E) $0.50
Suppose in Finland a worker can produce either 32 cell phones or 4 kayaks while in Canada a worker can produce either 40 cell phones or 10 kayaks
a. Which country has an absolute advantage in cell phone production? In kayak production? b. What is the opportunity cost of 1 cell phone in Finland? In Canada? c. What is the opportunity cost of 1 kayak in Finland? In Canada? d. Which country has a comparative advantage in cell phone production? In kayak production? e. Suppose each country has 1,000 workers. Currently, each country devotes 40 percent of its labor force to cell phone production and 60 percent to kayak production. What is the output of cell phones and kayaks for each country and what is the total output of cell phones and kayaks between the two countries? f. Suppose each country specializes in the production of the good in which it has a comparative advantage. What is the total output of cell phones and kayaks in the two countries? g. Provide a numerical example to show how Finland and Canada can both gain from trade. Assume that the terms of trade are established at 6 cell phones for 1 kayak.
One explanation for the fall in the value of the U.S. dollar since 2001is
a. the mix of an tight fiscal/tight monetary policy over the period. b. the relative weakness of the U.S. economy over the period. c. a higher degree of accommodation of supply shocks in the United States relative to our trading partners. d. the disintegration of the Bretton Woods system during these years.