Good A and good B are substitutes in production. The demand for good A increases so that the price of good A rises. The increase in the price of good A shifts the
A) demand curve for good B leftward.
B) demand curve for good B rightward.
C) supply curve of good B leftward.
D) supply curve of good B rightward.
C
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as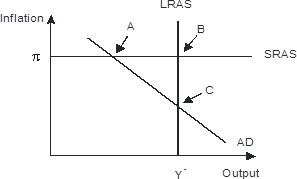
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward C. Aggregate demand shifting rightward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
Allocative efficiency refers to
A) producing the goods and services most highly valued. B) using the least amount of labor to produce output. C) producing the maximum possible amount of output. D) obtaining the least output with the most inputs. E) producing at any point on the PPF.
Justin has a part-time job and earns $50 per week. He spends his entire income on two goods: Hamburgers (which cost $2 each) and movie rentals (which cost $3 each). Draw Justin's budget constraint
Suppose that Justin decides to purchase 10 hamburgers and rent 10 movies this week. Is this choice within Justin's opportunity set? Show this choice on your graph.
An international lender of last resort creates a serious ________ problem because depositors and other creditors of banking institutions expect that they will be protected if a crisis occurs
A) moral hazard B) adverse selection C) public choice D) strategic choice