How are parasitoids different from typical brood parasites?
a. they are usually not insects
b. they affect only plants
c. they lay eggs inside a host, which is eventually killed
d. they fool another species into caring for their young
e. they usually only affect the eggs of birds
ANSWER: c
You might also like to view...
Type S Streptococcus pneumoniae bacterium is lethal and will kill its host. If heat inactivated the S strain becomes nonlethal. Type R Streptococcous pneumoniae is a nonvirulent strain of bacteria. What would occur if one were to inject both the R strain and heat-killed S strains into a host organism such as the mouse?
A. The S strain would be transformed into the nonvirulent R strain and kill the host. B. The R strain would be transformed into the virulent S strain and kill the host. C. The S strain would be transformed into the nonvirulent R strain and not affect the host. D. The R strain would be transformed into the virulent S strain and not affect the host. E. Neither the S nor the R strain would change.
Examine the figure above. In the continental U.S., the dark green patches show areas with the highest bird species richness. What best explains why these areas have such diversity?
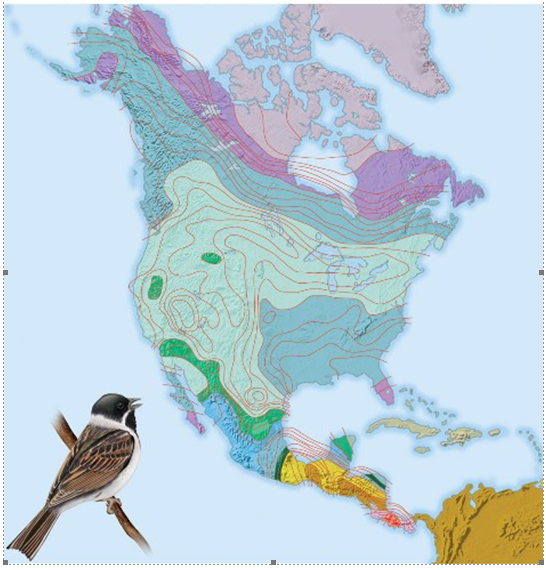
A. These areas have the highest temperatures in the continental U.S.
B. These areas have mountainous terrain.
C. These areas have well-protected natural areas.
D. These areas have low frequencies of extreme weather events and fire.
This animal is radially symmetric, has
nematocysts, and cnidocytes. This animal is ___.
a. a jellyfish b. an earthworm c. a sea anemone d. a sponge e. more than one of these
Referring to the above diagram, which
structure is responsible for secreting digestive enzymes into the small intestine and hormones into the blood?
a. D b. E c. F d. G e. A