If there are no profits in competitive equilibrium, why do firms produce? How can they stay in business?
The "no profits" conclusion of competition refers to economic profits-there is no excess rate of return to the typical firm. However, each firm is able to earn sufficient accounting profits to cover the opportunity cost of invested factors and to continue operating. The source of the confusion is failing to distinguish between accounting and economic profits.
You might also like to view...
An incentive is:
A. the marginal cost of engaging in a course of action. B. the marginal benefit of engaging in a course of action. C. something that causes people to behave in a certain way by changing trade-offs they face. D. rational behavior that involves thinking on the margin.
Which economic concept is the closest to the saying, "There's no such thing as a free lunch"?
a. Specialization b. Unlimited wants c. Underutilization of resources d. Opportunity costs e. Overutilization of resources
the amount of additional aggregate demand needed to achieve full employment after allowing for price-level changes
What will be an ideal response?
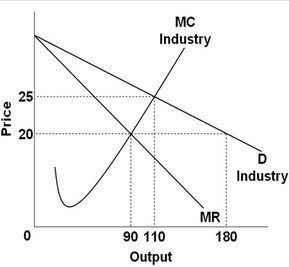 Based on the graph above, what is the difference between the purely competitive equilibrium level of output and the pure monopolist equilibrium level of output?
Based on the graph above, what is the difference between the purely competitive equilibrium level of output and the pure monopolist equilibrium level of output?
A. 20 units of output B. 90 units of output C. 5 units of output D. 70 units of output