This figure shows the motions of atoms (a) in a falling ball and (b) after the ball hits the ground. Why would you not expect the ball on the ground to suddenly move upward?
a. Because it is exceedingly unlikely that the velocities of the atoms would simultaneously reorder themselves to generally point upward.
b. It would violate the first law of thermodynamics.
c. Both a. and b.
a
You might also like to view...
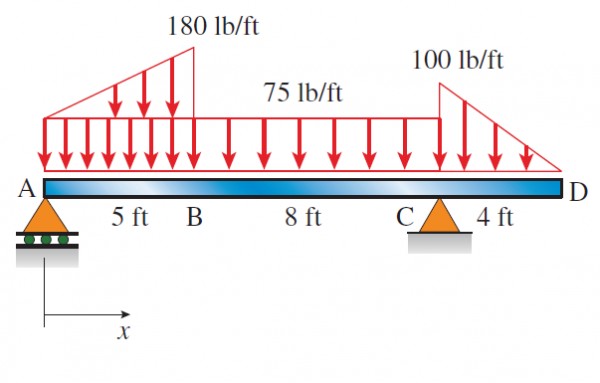
The distributed loading on beam ABCD is to be replaced by a statically equivalent set of forces. The mag- nitude and location of the statically equivalent force on beam segment AB are:
(A) 575 lb, 4.1 ft
(B) 638 lb, 4.2 ft
(C) 740 lb, 3.9 ft
(D) 428 lb, 4.4 ft
Newton's version of Kepler's third law states: p2 = × a3 In this equation, what does a represent?
A) the orbital period B) the average distance between the two objects C) the masses of the two objects D) the universal gravitational constant
What would you have to change about the Earth to stop our planet from having significantly different seasons?
What will be an ideal response?
Which method relies on the mass of a dark object revealing its presence?
A) pulsars slowing down irregularly B) temporary brightening of a distant star by a gravity lens C) asteroidal occultations D) stellar eclipses E) ring occultations