Megan is trying to decide whether to buy house insurance for her home in Miami. Her house is worth $200,000 and analysts have determined that the average loss from a Hurricane could be $45,000. They have also determined there is a 50 percent chance that she will face a hurricane. Suppose Megan is a risk averse person with a utility-of-income function such as the one given below. If the policy costs $22,500, Megan will 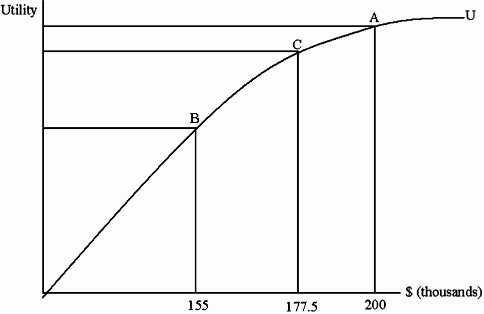
A. be indifferent between buying or not buying the insurance.
B. not buy the insurance.
C. buy the insurance.
D. we can't say.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
When prices drop in response to a decline in demand for an increasing cost industry:
a. producer surplus will increase but rents may decrease. b. rent earned by elastically supplied inputs will decline by more than rent earned by inelastically supplied inputs. c. rent earned by elastically supplied inputs will decline by less than rent earned by inelastically supplied inputs. d. both producer surplus and rents will increase.
The social rate of discount is best approximated by:
a. the cost of government borrowing b. the opportunity cost of resources taken from the private sector c. 3 percent d. 30 percent e. none of the above
If nominal GDP is $954 billion and velocity is 9, then the money supply: a. is $106 billion
b. is $122 billion. c. is $98 billion. d. is greater than $8 trillion.
A contractionary monetary policy is most likely to reduce output with little impact on inflation when the economy
a. is near full employment and the aggregate supply curve is horizontal. b. is near full employment and the aggregate supply curve is vertical. c. has substantial unemployment and the aggregate supply curve is vertical. d. has substantial unemployment and the aggregate supply curve is horizontal.